In an era marked by rapid technological advancements and a demand for high efficiency, Industrial Automation Solutions have emerged as critical tools for optimizing manufacturing, improving productivity, and ensuring precision. These solutions replace or assist human labor with machines, software, and control systems—revolutionizing how industries operate.
What Is Industrial Automation?
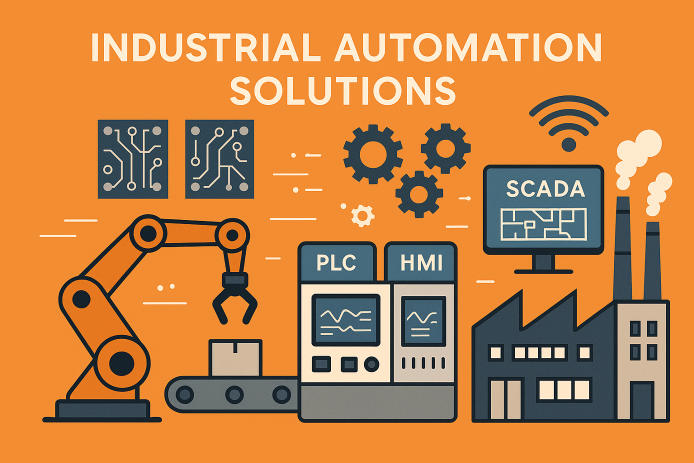
Industrial automation refers to the use of control systems—such as computers, robots, and information technologies—to handle different processes and machinery in an industry. The goal is to improve efficiency, accuracy, consistency, and safety in operations, often with minimal human intervention.
Automation solutions can range from simple relay-based controls to complex networks of PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, industrial robots, and AI-driven analytics platforms.
Core Components of Industrial Automation
- Sensors and Actuators
Sensors detect physical parameters (e.g., temperature, pressure, position), while actuators perform actions based on control system commands (e.g., motors, valves). - Controllers (PLCs and DCS)
PLCs and Distributed Control Systems (DCS) execute programmed logic to manage machinery and processes. - Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
Interfaces that allow operators to monitor and control industrial processes visually. - SCADA Systems
These systems provide centralized control and real-time data visualization, often across entire facilities. - Robotics and Cobots
Robots automate repetitive or hazardous tasks, while collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside humans safely. - Industrial Networks and IoT
Devices and machines communicate via industrial protocols (e.g., Modbus, Profibus) and IoT platforms for better data-driven decision-making.
Benefits of Industrial Automation
- Increased Productivity: Automation enables 24/7 operation with fewer errors and higher throughput.
- Enhanced Quality and Consistency: Reduces variation and human error, ensuring uniform product quality.
- Improved Safety: Removes humans from dangerous tasks and environments.
- Operational Cost Reduction: Though initial investment is high, long-term savings come from reduced labor and waste.
- Data Collection and Insights: Advanced automation integrates data analytics for predictive maintenance and process optimization.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Modern systems can quickly adapt to new products or production volumes.
Key Industries Using Industrial Automation
- Automotive: Robotic assembly lines and AI-driven QC systems.
- Electronics: High-speed PCB assembly and testing.
- Pharmaceuticals: Precision dosing, packaging, and compliance control.
- Food and Beverage: Processing, bottling, and packaging automation.
- Energy: Power grid automation, remote monitoring of substations.
- Aerospace: CNC machining, material testing, and documentation.
Challenges in Industrial Automation
- High Initial Cost: Implementing automation requires significant upfront capital.
- Workforce Displacement: Transitioning from manual to automated systems can lead to job losses if not managed properly.
- System Integration: Merging new systems with legacy infrastructure can be complex.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased connectivity raises vulnerability to attacks.
- Maintenance and Skill Gaps: Advanced systems require skilled technicians for upkeep and troubleshooting.
Emerging Trends in Industrial Automation
- AI and Machine Learning: Predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and process optimization.
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of physical systems for simulation and diagnostics.
- Edge Computing: Processing data locally on devices for faster responses.
- Sustainable Automation: Energy-efficient systems and smart resource management.
- 5G and Advanced Connectivity: Faster, more reliable machine-to-machine communication.
Conclusion
Industrial automation is not just about machines replacing humans—it’s about redefining how industries operate in terms of efficiency, safety, and adaptability. From robotics to cloud-based control systems, the scope and power of automation continue to expand, offering businesses a competitive edge and laying the foundation for the factories of the future.
Would you like a full-length version of this article (2000+ words) with a custom infographic or case studies?